Types of Polymers
Polymers are materials with long molecular chains, divided into three categories: natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic polymers. These materials, with diverse structures and properties, are used in various industries, from plastics and rubber to textiles, medicine, electronics, and advanced technologies. Biodegradable polymers have gained more importance due to environmental concerns. Additionally, smart polymers and nanopolymers play a key role in modern technologies.
Introduction
Polymers are fascinating and versatile materials that are widely present in our daily lives. These materials are made up of long chains of molecules, giving them unique properties. Polymers, also known as macromolecules, exist both naturally and are produced synthetically. From plastics to natural fibers, these materials are used in various places and have diverse applications.
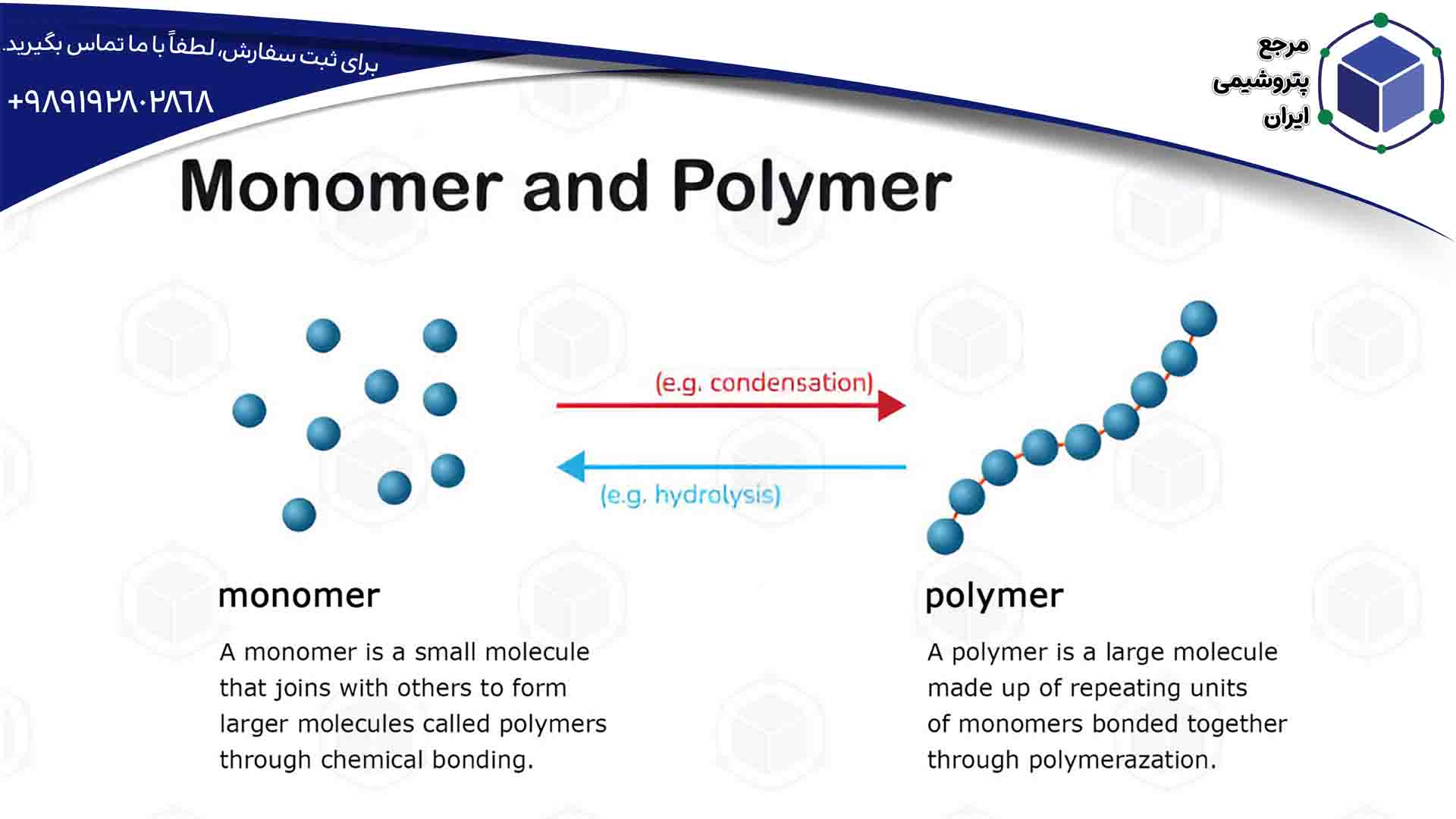
What is a Polymer?
Polymers, also called macromolecules, are composed of small units called monomers, which are connected in chains. These chains can be linear, branched, or networked. The properties of polymers depend on the type of monomers, the structure of the chains, and how they are connected. Understanding these structures is crucial for designing materials with specific characteristics.
Types of Polymers Based on Structure
The molecular structure of polymers greatly influences their properties. Linear polymers consist of straight chains and are usually flexible. Branched polymers have main chains with side branches, which can affect their physical properties. Networked polymers are made up of chains connected crosswise, making them stiffer and more resistant.
Classification by Type
Polymers can be divided into three main categories: natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic. Natural polymers like cellulose, protein, and starch are found in nature. Semi-synthetic polymers are obtained through chemical modifications of natural polymers, such as cellulose acetate. Synthetic polymers are produced in laboratories and factories, such as polyethylene and nylon.
Classification by Application
Polymers have numerous applications. Plastics, which are a type of polymer, are used in making containers, packaging, and various components. Elastomers, or rubbers, have elastic properties and are used in producing tires and rubber products. Fibers, which have a high length-to-diameter ratio, are used in the textile industry.
Methods of Producing Polymers
Polymers are produced through a process called polymerization, which is carried out in two main ways: addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. In addition polymerization, monomers quickly bond to form the polymer chain. In condensation polymerization, two different types of monomers react together, usually releasing a small molecule like water.
Properties of Polymers
Polymers have different properties depending on their molecular structure. Some are hard and resistant, while others are soft and flexible. Polymers can be good thermal and electrical insulators or resistant to chemicals. This diversity in properties allows polymers to be used in various applications.
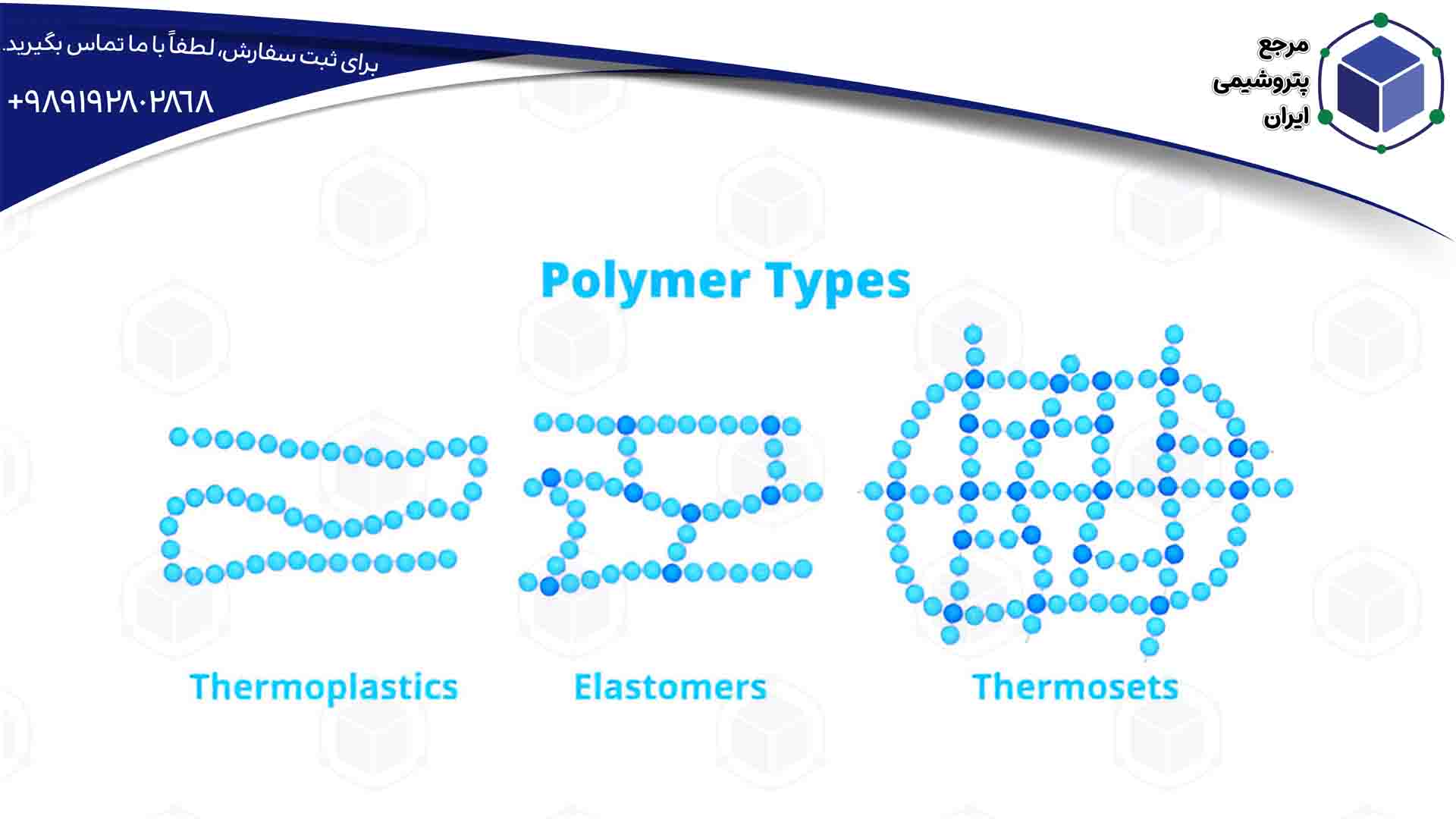
Thermoplastics and Thermosets
Polymers are divided into two types: thermoplastics and thermosets. Thermoplastics soften when heated and can be reshaped, making them suitable for recycling. Thermosets, on the other hand, do not melt after the initial shaping and usually have higher heat resistance.
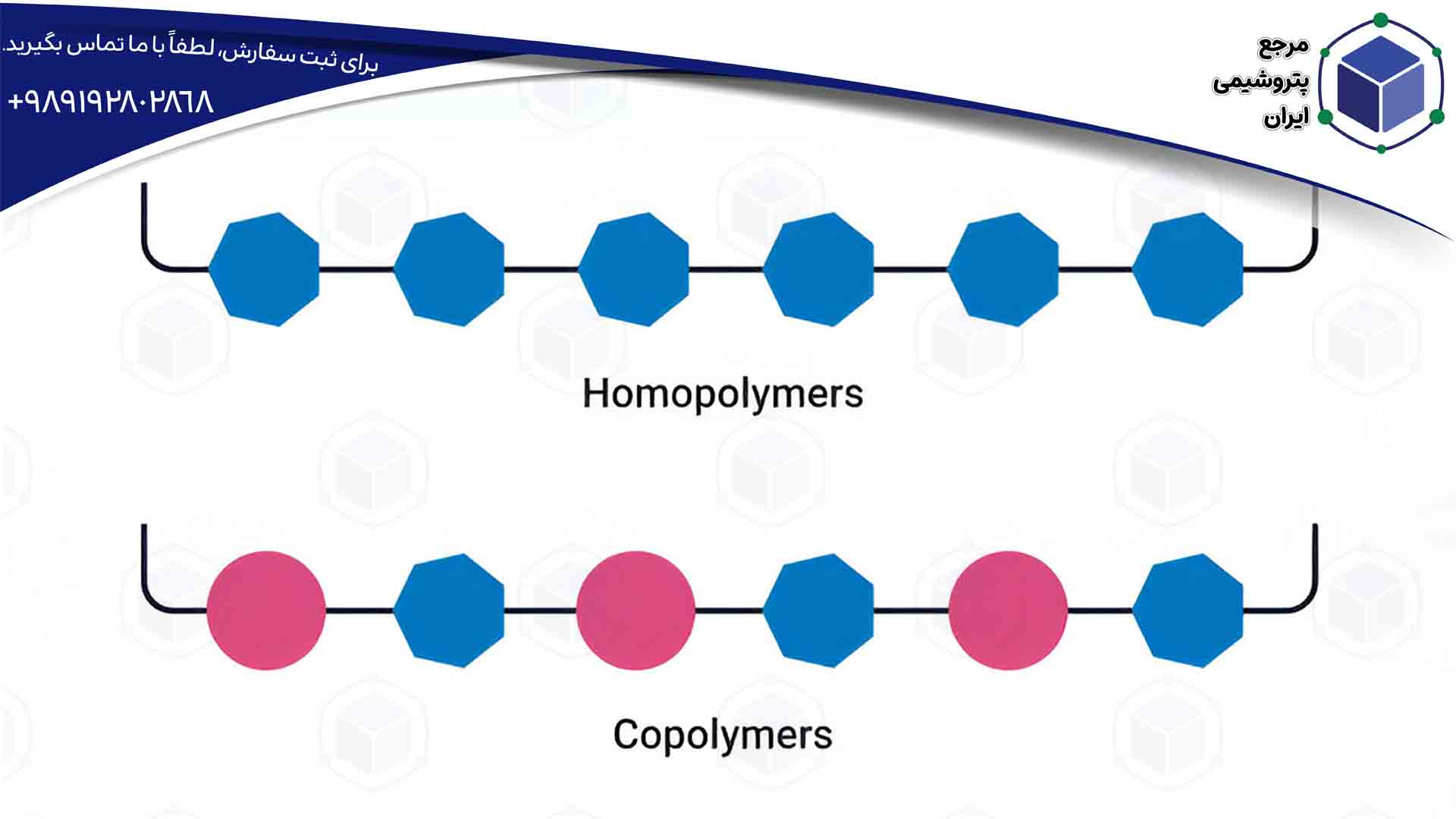
Copolymers and Homopolymers
Polymers are also classified based on the type of monomers they are made of. Homopolymers consist of repeating units of a single type of monomer, such as polyethylene. Copolymers are made up of two or more different types of monomers and have combined and unique properties.
Biodegradable Polymers
Due to environmental concerns, there has been increased attention on biodegradable polymers. These polymers are broken down by microorganisms and converted into natural materials. An example is polylactic acid (PLA), which is used in packaging and single-use products.
Challenges and Future of Polymers
Despite the many advantages of polymers, they have also caused issues such as environmental pollution. Therefore, extensive research is being conducted to develop eco-friendly polymers and improve recycling methods. Additionally, with advancements in nanotechnology, new opportunities have emerged for designing and using polymers.
Smart and Advanced Polymers
Smart polymers respond to external stimuli such as heat, light, or moisture and are used in drug delivery systems and sensors. Conductive polymers are also used in electronics and solar cells.
Conclusion
Polymers play a significant role in modern life and are used in various industries, from packaging to medicine and electronics. With scientific and technological advancements, it is expected that these materials will find more applications in the future and contribute to the development of sustainable and eco-friendly technologies.