What is a Compound?
Compound granules are a type of pre-engineered plastic material made by combining polymers with various additives (such as pigments, stabilizers, and reinforcements). These granules are provided to manufacturers for use in injection molding, extrusion, and other forming processes to create diverse plastic products.
What is a Compound
Why are Polymer Compounds Valued Across Industries?
Compounds are materials formed by blending multiple raw components to enhance mechanical, chemical, or thermal properties. These materials are widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, electrical appliances, and packaging. By offering high resistance, flexibility, and durability, compounds improve the quality of end products while reducing production costs.
Key Features of Compounds
The most important features of compounds include high mechanical resistance, flexibility, thermal stability, and optimized chemical properties.
A compound consists of three main components used to enhance product characteristics: Polymer Base, Compatibilizing Agent and Various Additives
To achieve the desired blend, the compound must be added to a product that already has a polymer base, ensuring seamless integration. The compatibilizing agent facilitates uniform mixing of the compound with the product; otherwise, the dispersion of the compound in the polymer matrix will be ineffective. The third component (additives) enhances the final product’s properties and may alter its color in some cases.
Due to their precise formulation, compounds exhibit exceptional resistance to harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, they improve the visual and physical properties of products while reducing overall weight. Given these advantages, a thorough understanding of compound characteristics is essential for many industries, driving their expanding adoption. Now that we know “what a compound is,” a detailed analysis of its properties becomes even more critical.
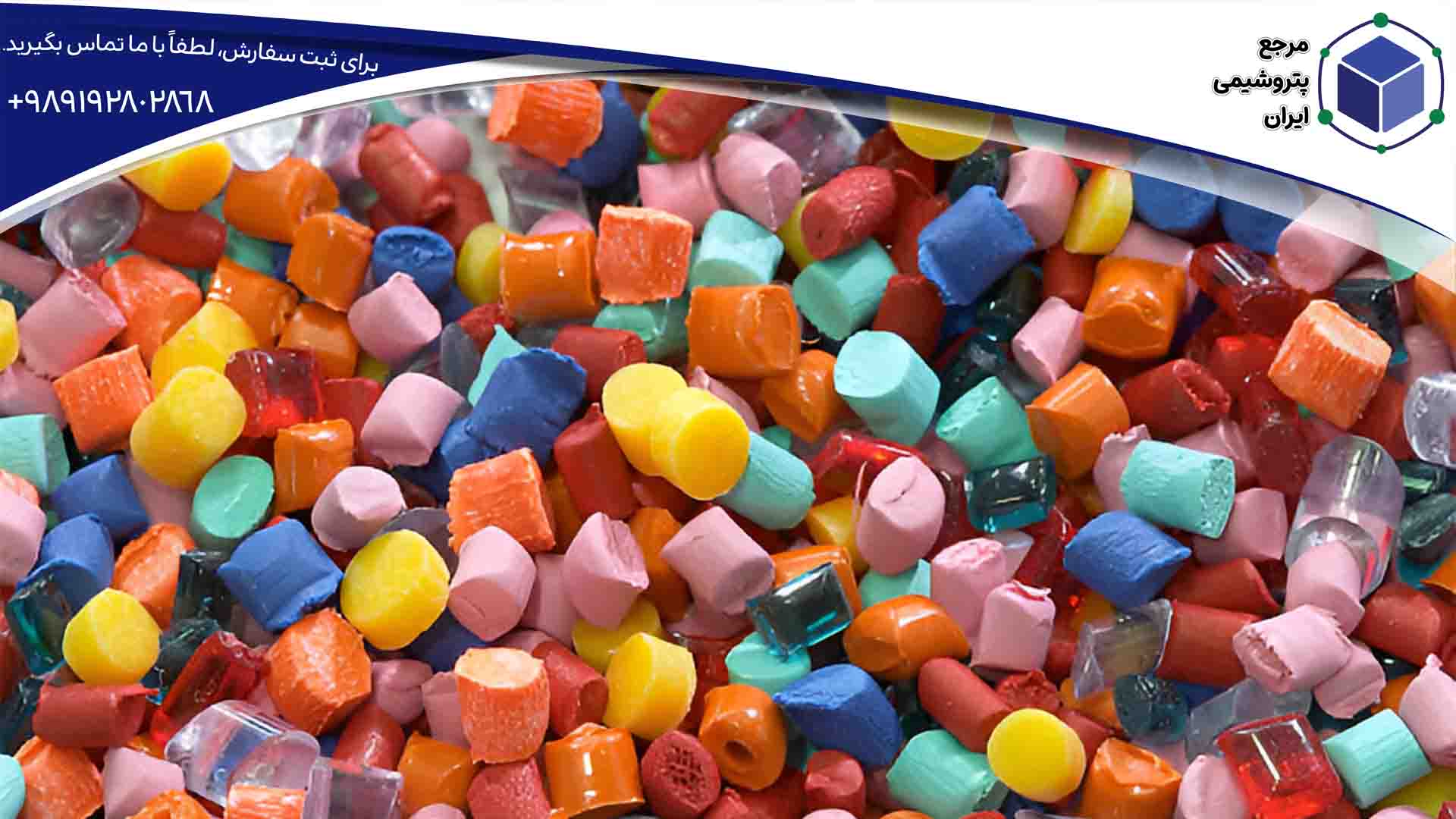

Types of Compounds
Below are detailed explanations of different types of polymer compounds and their applications.
1. Polyethylene and Polypropylene Compounds
These are two of the most widely used polymer compounds in the industry, discussed separately below.
Polyethylene compounds are produced in various densities and grades, offering features such as high resistance to pressure, impact, and sunlight. By adding pigments and reinforcing agents, these compounds are used in manufacturing products such as blown films (plastic bags), irrigation pipes, and pressure pipes. The inclusion of pigments and carbon black in these compounds enhances the durability and UV resistance of the final product.
- Polypropylene Compounds
Polypropylene is a tough and ductile polymer with low density, used in household goods, kitchenware, pipes, and automotive components. This compound is highly effective in applications requiring chemical and mechanical resistance due to its excellent moldability and flexibility. Polypropylene compounds are available in various colors and grades to meet diverse application needs.
2. Glass Fiber-Reinforced Compounds
These compounds are reinforced with glass fibers to provide higher mechanical strength and thermal resistance. They are widely used in the automotive, electrical, and household appliance industries. Due to their high thermal resistance, these compounds are ideal for manufacturing components that require strength and stability at elevated temperatures. They are also utilized in coatings and insulation products needing mechanical and thermal protection.
3. Rheological Cleaning Compounds
Rheological cleaning compounds are utilized for their unique flow properties in cleaning extrusion equipment and molding machines. These compounds are employed in polymer product manufacturing processes, such as polyethylene films and pipes, to clean the cylinders and screws of machines from residual materials and enable color changes in products. One of the primary advantages of these compounds is the reduction in waste generated during the cleaning process.
4. Filler Compounds and Calcium Carbonate
Filler compounds are produced by adding various percentages of fillers, such as calcium carbonate, to polymer bases. Calcium carbonate enhances the strength and durability of polymer materials while reducing production costs. These compounds are particularly used in extrusion, plastic injection, and thermoforming processes to manufacture diverse products like sheets and pipes. Adding calcium carbonate to products not only reduces costs but also improves impact strength and heat resistance.
5. Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Compounds
These compounds are made with a high percentage of barium sulfate and a polypropylene base and are used in applications requiring thermal or acoustic insulation. For example, they are utilized in the production of sewage pipes, construction structures, and buildings that require soundproofing. The acoustic insulation properties of these compounds play a vital role in reducing environmental noise and creating a quieter atmosphere.
6. Special Compounds
Below are some other types of polymer compounds.
- Flame-Retardant Compounds
These polymers are formulated to reduce the risk of fire and are used in industries such as electronics, automotive, furniture, and the manufacture of electrical equipment requiring high safety standards.
- Biodegradable Compounds
These compounds are employed to produce disposable products and eco-friendly packaging, contributing to the reduction of non-degradable waste.
- Antioxidant Compounds
This type of compound increases the resistance of polymer materials to oxidation and thermal degradation by incorporating antioxidants and thermal stabilizers. These compounds are used in industries such as oil and gas, pipelines, and electrical components.
- Polyamide and Polycarbonate Compounds
Polyamides are utilized in automotive parts and electrical equipment due to their strength and heat resistance. Polycarbonates, known for their transparency and high durability, are employed in the production of lenses, optical enclosures, and impact-resistant automotive components.
In summary, each of these compounds contributes to improved performance and durability of products in various industries. The choice of compound depends on the type of product and its specific requirements. We’ve explored the question of “What is a compound?” and its various types. Next, we will examine the most commonly used compounds.
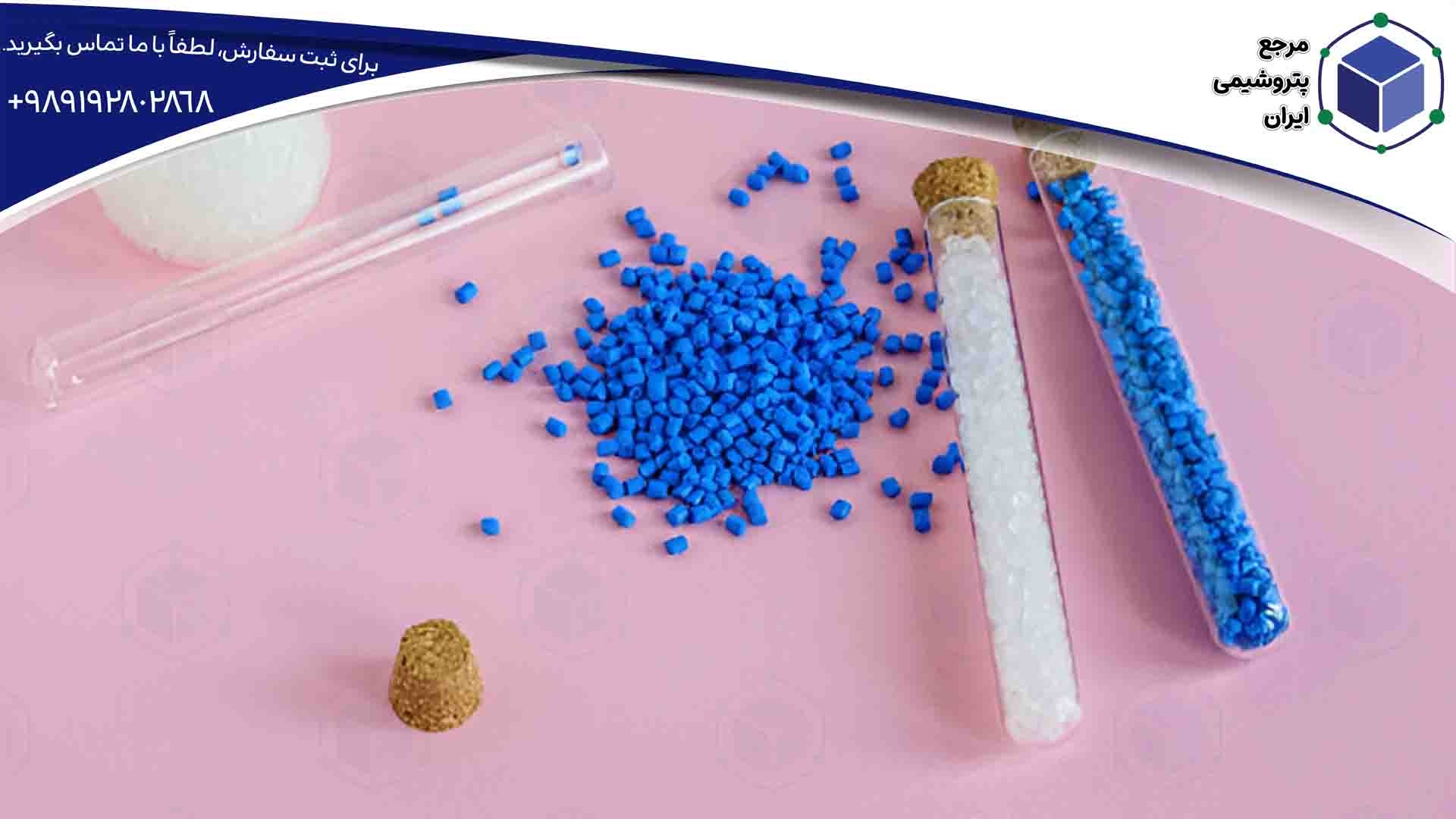

Most Common Compounds
The most widely used polymer compounds include polyethylene and polypropylene, which are utilized in various industries due to their unique physical and mechanical properties.
Polyethylene compounds, strengthened by additives like pigments and fillers, are used in the production of polymer films, durable pipes, packaging, and automotive parts. Meanwhile, polypropylene compounds, with their high ductility, lightweight, and resistance to corrosion, are ideal for household items, pipes, fittings, and automotive components. These compounds, enhanced with diverse additives, can withstand various working conditions and are highly valued in the industry for their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Understanding their extensive applications gives us a clearer answer to the question “What is a compound?” and highlights their significance.
Advantages of Compounds
The use of polymer compounds in various industries offers numerous advantages due to their unique capabilities, improving the quality and performance of products. Below are the key benefits of using these compounds.
Enhanced Strength and Durability
Reinforcements like glass fibers or nanoparticles significantly increase the strength and durability of materials, which is crucial for industrial applications such as automotive parts and construction materials.
Improved Thermal Properties
Adding thermal stabilizers enables polymers to withstand higher temperatures, a key requirement in automotive and electronics industries.
Improved Electrical Properties
Additives with insulating properties enhance the electrical insulation quality of polymers. Additionally, incorporating metallic nanoparticles can improve their electrical conductivity.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical-resistant additives increase the ability of polymers to withstand chemical damage, making them highly valuable in chemical and medical industries.
Cost Reduction
The use of cost-effective fillers can lower production expenses while maintaining desired material properties.
Innovative Product Design
Combining various materials and additives facilitates the creation of new materials with enhanced properties, driving innovation in industries and new product designs.
What new features do additives bring to base polymers that make polymer compounds so popular?
With the mass production of products, plastics have become a primary component of many items. However, the price and standard properties of plastics cannot meet all needs. Therefore, manufacturers strive to modify and improve the initial characteristics of plastics. Here, the compounding industry emerges as an effective solution.
Iran Petrochemical Reference, as a producer of plastic compound products in Iran, aims to meet market and customer needs by enhancing various features in plastics.
Creation of new features
Modification and reinforcement of base properties
Cost and pricing adjustments
These features include color, strength, stability, impact resistance, thermal resistance, and many other physical and chemical specifications.
For example, PP 8051 is one of Iran Petrochemical Reference’s compound products, where polypropylene is combined with calcium carbonate (CaCO₃). The production process of this product preserves the polymer’s original properties while enhancing its stiffness and thermal resistance.
Understanding the advantages of compounds further helps clarify “What is a compound?” In the following section, we will highlight the applications of compounds in various industries.
Applications of Compounds
Compounds, as combinations of various materials, help shape specific properties and improve product performance across diverse industries. With their capabilities, these compounds can meet different needs in mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical domains. Below are prominent applications of polymer compounds in various industries:
Automotive Industry
The use of polymer compounds such as polypropylene and ABS in the production of interior and exterior automotive components is widespread. These compounds, known for their wear and heat resistance, reduce vehicle weight and contribute to improved fuel efficiency.
2. Electronics
Special compounds are widely used in the production of electronic equipment, including circuit boards and protective housings. These materials, due to their insulating properties and high thermal resistance, are considered ideal for this industry.
Packaging Industry
In the packaging industry, compounds are used in the production of containers and bottles due to their resistance features. They can protect against chemical and thermal exposure.
Construction Industry
In construction, polymer compounds help in the production of insulation materials, profiles, and pipes. These materials, due to their strength and resistance to weather conditions, are considered valuable options for buildings.
Medical Industry
In medical equipment, polymer compounds are increasingly used due to their biocompatibility and high sterilizability. These materials are used in the production of surgical tools and medication packaging.
Household Goods
Many household products, including furniture and sports equipment, benefit from compounds. These compounds perform better than regular plastics due to their strength and visual appeal.
Overall, polymer compounds, as versatile and efficient materials, are recognized as a key option in producing high-quality, durable products across various industries. So, when asked “What is a compound?”, now you know which industries they are used in.

Stages of Polymer Compound Production
The production of polymer compounds is a multi-stage process that begins with the selection of raw materials and leads to the production of the final product. Below are these stages explained briefly:
Selection of Raw Materials
The compound production process starts with the selection of a suitable base polymer and the desired additives. This choice is made based on the required properties for the final application. At Exir Polymer Company, the focus is on ensuring that the selected materials are blended optimally with polypropylene, polystyrene, or ABS.
Weighing and Mixing
After determining the materials, they are weighed according to a precise formula to maintain the correct ratio of additives to the base polymer. Then, these materials are mixed in a twin-screw extruder. At this stage, the materials are ground and heated to improve the quality of the engineered plastic. Additionally, a vacuum is created in the machine to expel gases produced during the process, preventing the formation of microbubbles.
Extrusion
The mixed materials are transferred to an extrusion machine, where they are melted and homogenized. This step is crucial to ensure the uniformity of the materials and prevent any inhomogeneity.
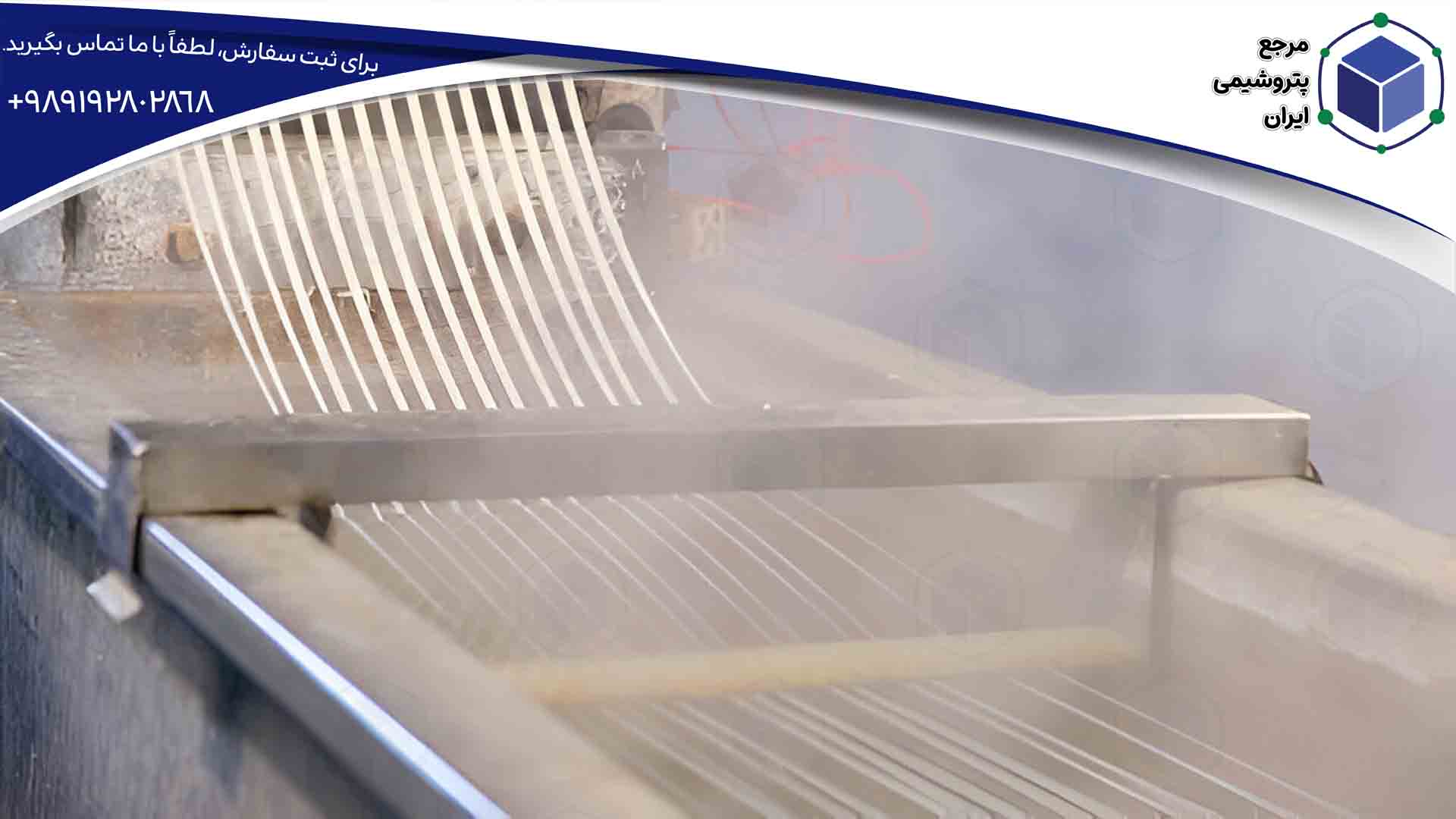

Production of Polymer Granules
After the extrusion process, the molten mixture is cooled and shaped into solid granules. These granules are then re-melted and molded into the final products.
Finally, compounds are produced through these precise steps under controlled conditions. The first step involves melting the raw materials in the extruder, where the powdered base polymers and additives are converted into a melt. Then, these materials are cooled during the cooling process and prepared for cutting into appropriate sizes. The final products are stored under specific conditions to evaluate their quality before being released to the market. These stages demonstrate what a compound is and how it is produced.